This tour will take you from Antananarivo to Andasibe, Tsingy de Bemaraha and Morondava :
-
Andasibe – Mantadia National park
Andasibe–Mantadia National Park is about 150 km to the east from Antananarivo, along the RN2, and it can be reached in 3 to 4 hours by car. Comprising two distinct protected areas: Analamazoatra Special Reserve and Mantadia National Park, Andasibe-Mantadia National park is one of the most frequently visited site in the country, and one of the best places to observe lemurs in Madagascar.
Fauna
It is also one of the best primate-watching site in the world. This site is known to be the refuge for a wide variety of lemur species (14 diurnal and nocturnal species), including the famous Indri Indri, the Aye-Aye, the goodman’s mouse lemur, the Crossley’s dwarf lemur, the Eastern woolly lemur sifaka, and sometimes southern black-and-white ruffed lemur. 51 reptile species, 84 amphibian species, 72 mammal species, 117 bird species, and countless insectivorous bats that have been recorded. Mantadia is the one of the best birdwatching site on the Big Island.
Flora
About the flora, with its lush and green vegetation this protected area contains a collection of evergreen vegetation epiphytic plants (plants living on other plants), palm trees, mosses, fern, bamboo, hardwoods, and precious woods, and pandanus. This park is also famous for its orchids with 120 inventoried species, entirely endemic. They bloom between September and January.
Located in the western part of Madagascar, about 200 kilometers from Morondava, the protected area of Bemaraha covers more than 150,000 hectares. It is home to the famous Tsingy de Bemaraha National Park, one of the most spectacular landscapes of Madagascar and even of the world. The famous Tsingy de Bemaraha National Park is the first tourist attraction that makes the western destination of Madagascar a popular destination for tourists.
Tsingy
Indeed, the Tsingy are a group of limestone rocks whose formation began several million years ago when the sea still covered the region. Thus, corals and shells have stacked and welded together to form thick layers which have subsequently raised. In the open air, the limestone cracked to give rise to diaclases and canyons. Rainwater that has an acid characteristic has also contributed to erosion by shaping tapered slats and deep tunnels with concretions on the surface.
Limestone
It is a true limestone cathedral characterizing one of the most spectacular natural landscapes of the Great Island and even of the world, hence it’s inscription to the world natural heritage and national cultural heritage of UNESCO. Tsingy de Bemaraha is strongly regarded as a place of endemism because of their richness in plant and animal species where scientists have recorded a high level of endemism of around 80-90%.
Fauna
The protected area of Bemaraha is a true refuge for rare and endemic animal species. There are 17 rare species of reptiles, including the very small chameleon scientifically called the Brookesia perarmata and a species of rodents, Nesomys lambertoni, found only in the park. There are also 11 species of lemurs, six species of birds, and two species of local endemic amphibians.
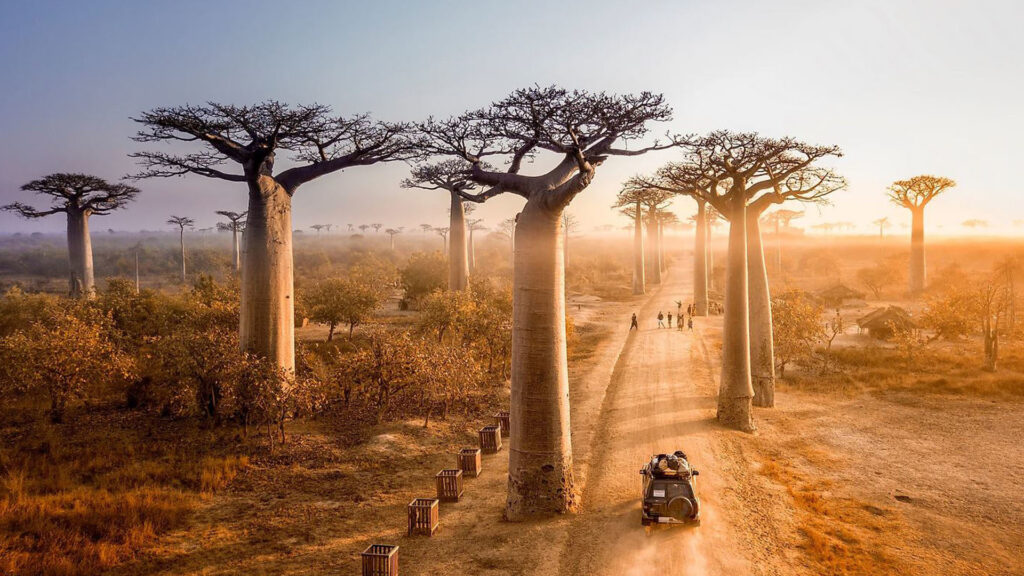
On the flora side, the park abounds with more than 600 species of plants, but the baobabs, aloes and flamboyants remain the first stars.
About ten trees 30 meters high border this avenue, of the species Adansoniagrandidieri, endemic to Madagascar. Baobabs, over 800 years old, known locally as
Renala (in Malagasy for “mother of the forest”), are a heirloom of the dense tropical forests that thrived in Madagascar.
The trees did not grow in isolation in this dry and bushy landscape but were part of a dense forest which has now disappeared (only 10% of primary forests remain in the country).
Over the years, with the increase in the country’s population, forests have been cut down for agriculture, leaving only baobab trees, which locals preserve both out of respect and for their value as a source of food and materials of constructions.